Non-IT Incidents: A Holistic Service Approach
When we think about incident reporting, the first association is often with IT-related disruptions. However, incident reporting holds equal significance for non-IT incidents that can occur in various aspects of an organization's operations. From workplace accidents to customer service mishaps, non-IT incidents demand a structured approach to reporting and resolution. Let's explore the positive and negative impacts of incident reporting in non-IT contexts.
Positive Impacts of incident reporting include but are not limited to:
- Employee Safety and Well-being
Incident reporting in non-IT areas, such as workplace accidents or safety hazards, prioritizes employee well-being. By promptly reporting incidents, organizations can implement safety measures and protocols to prevent future occurrences, fostering a culture of safety and care.
- Legal and Standards Compliance
Incident reports are crucial for compliance with regulations and legal requirements. Proper documentation of non-IT incidents helps organizations demonstrate due diligence, minimizing legal risks and potential penalties.
- Building Access and Security
Incident reports provide valuable insights into unauthorized access to rooms, systems and properties. By analyzing incidents where unauthorized individuals have access to areas which they should not, organizations can identify areas that require improvement, leading to more personal security and less theft and property damage.
Negative Impacts of not reporting incident include but not limited to:
- Reputation Damage
Unaddressed incidents can harm an organization's reputation. Whether it's a public safety issue or a customer service failure, negative incidents that are not properly reported and managed can erode trust among stakeholders.
- Operational Disruptions:
All incidents can disrupt normal operations, affecting productivity and service quality. Delayed reporting and resolution may lead to recurring disruptions, impacting the organization's bottom line.
- Lost Opportunities for Improvement
Neglecting incident reporting in non-IT areas deprives organizations of opportunities to learn and grow. Without proper documentation, valuable lessons that could lead to process enhancements may be lost.
Best Practice Reporting
Here is a best practice guide for responding to an Incident by reporting to the Incident Response Team (IRT).
Report
- Determine whether the incident is isolated
- Look for factors explaining abnormal behavior
- Estimate potential impact
IRT Follow-up Investigation
- Classify incident into Level 1 , 2 or 3
The following descriptions can be used to determine what response the IRT will take:
Level 1: Indicates attempted suspicious activity that did not cause harm, disrupt or have a felt impact. Limited impact or minor disruption to business operations. Isolated event (single observation).
Level 2: Indicates suspicious activity that deviates from normally observed behavior and, depending on the use case, may be indicative of a recurring or moderate issue that may have moderat ramification, important or moderate impact, or significant disruption to business operations.
Level 3: Indicates the issue is an immediate and threating event, which is compromising. Negative impact to business reputation, negative client reaction, financial and liability impacts.
- Contain and isolate
- Send template response to other partners
IRT Resolution
- Send a template response to other partners
IRT Review and Analysis (pending 1 Week after Resolution)
- Review all evidence collected
- Review investigation tracking
- Analyze results of the investigation conducted
- Determining the root cause of the incident
- Evaluate Incident Response Plan effectiveness
- Evaluate security controls to determine their appropriateness for the current risks
- Identified areas in which the plan, policy, or security control can be made more effective or efficient, and updated accordingly
At every step, it's essential to communicate the incident details to key stakeholders.
Example Report
Incident report
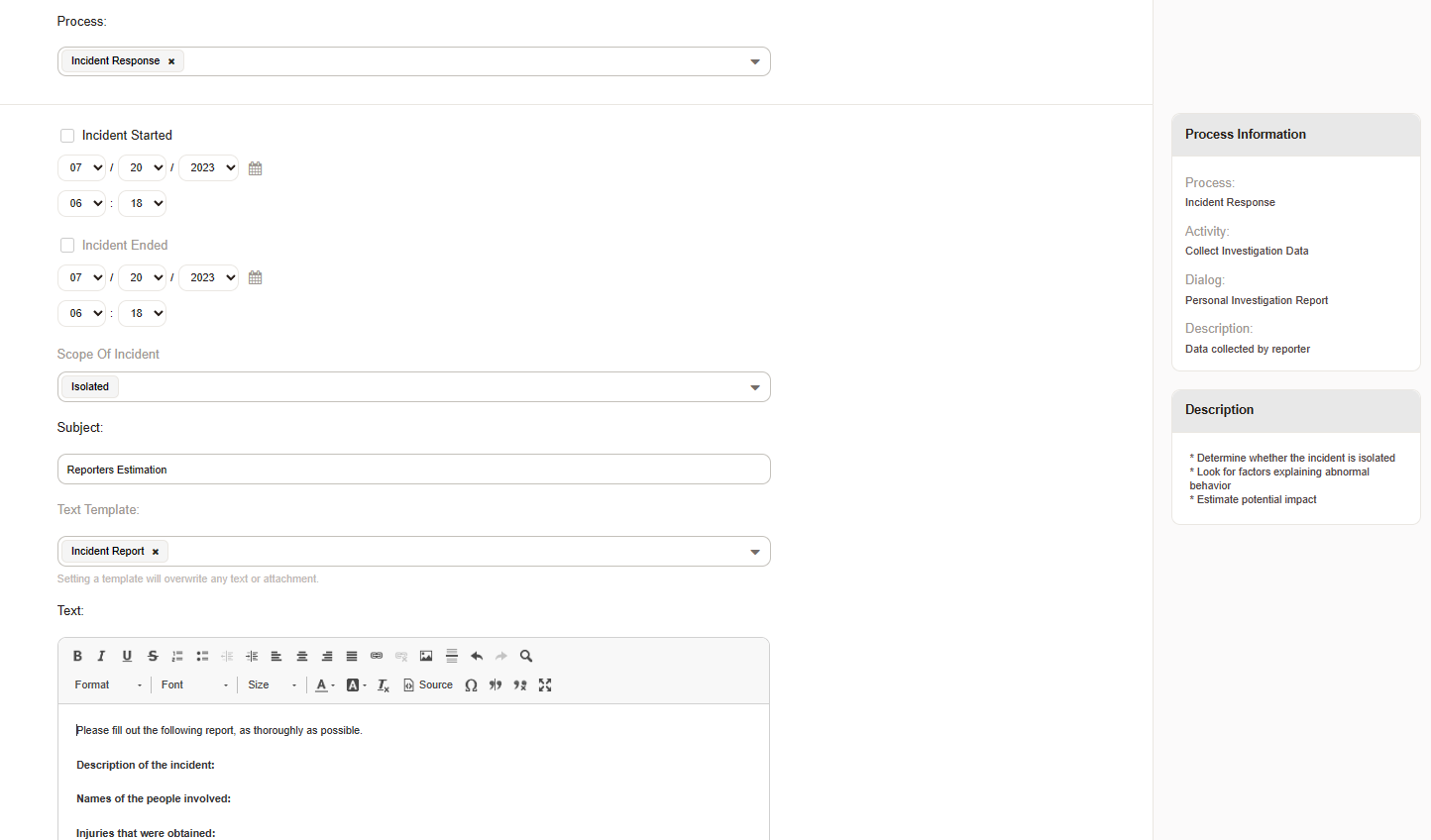
Znuny allows you to collect data for the report in dynamic fields, as well as use templates to pre-format response elements.
Date and time of the incident: 7/19/2023 at 10:00 PM
Location of the incident: Main entrance of the building
Description of the incident: An unauthorized individual gained access to the building by tailgating an employee.
Names of the people involved: The unauthorized individual and the employee who was tailgated.
Injuries that were obtained: No injuries were reported.
Medical treatment that may have been required: No medical treatment was required.
Equipment that was involved: None.
Investigation
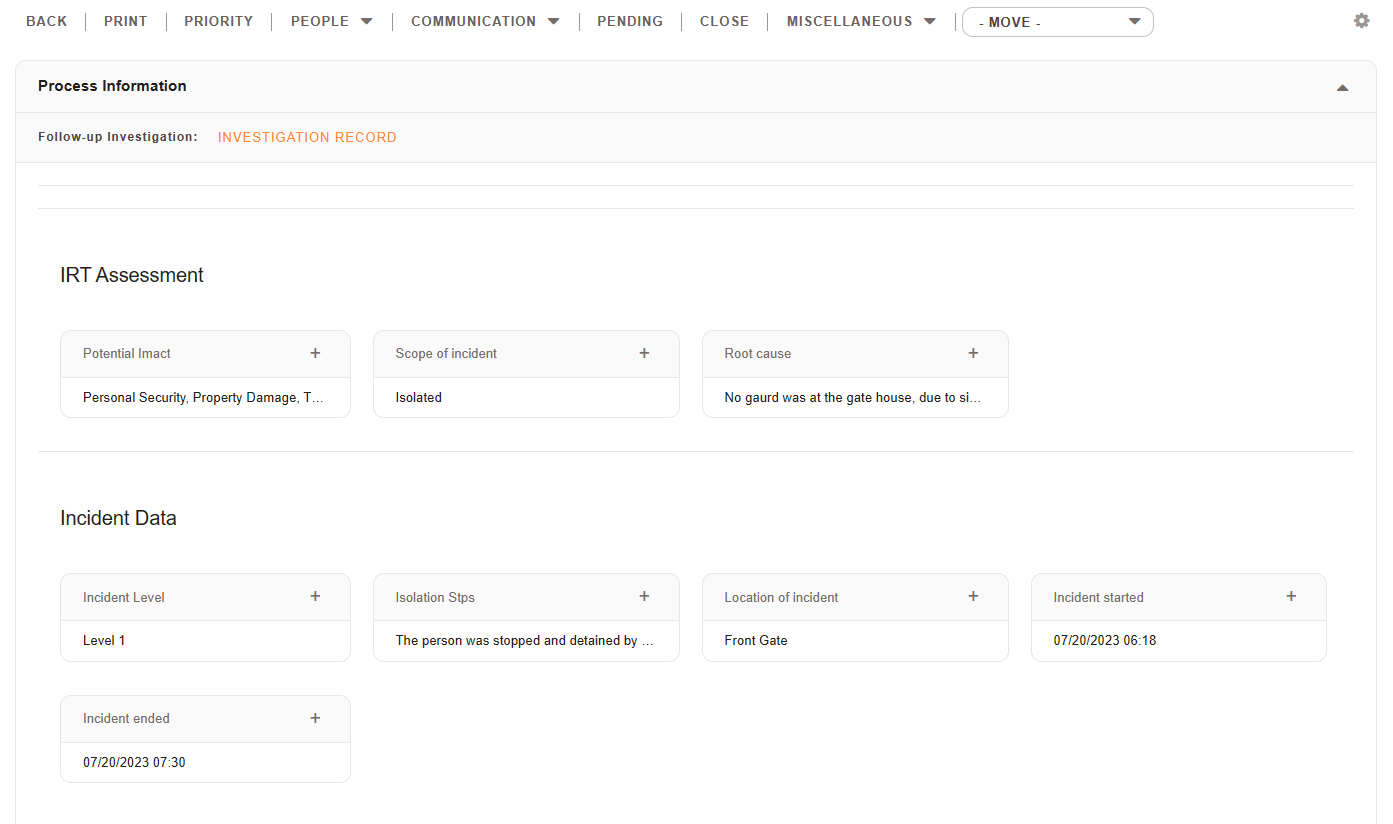
Again, the use of dynamic fields will help when it comes to reporting and keeping all your relevant information viewable during the entire process.
Impact of the issue: The incident had a negative impact on the security of the building and its occupants.
Root cause analysis: The root cause of the issue was identified as a lack of security awareness among employees.
Corrective actions taken: The employee who allowed the unauthorized individual to enter the building was reprimanded and additional security training was provided to all employees.
Review
Using the data collected, it's possible for the team to finalize the report.
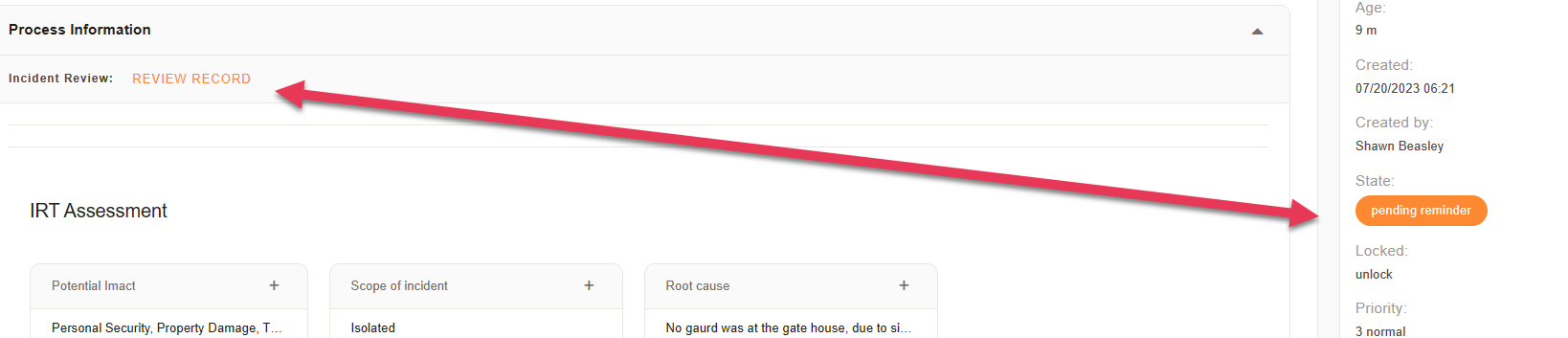
Preventive actions taken: A new security policy was implemented, requiring all employees to scan their ID badges when entering the building.
Review
Lessons learned: The incident highlighted the importance of security awareness training for all employees and the need for a more robust security policy.
Want to try this process, download the files here (you must import the Dynamic Fields first)
To see all the possibilities, read our documentation, contact our community, or get commercial support.
